The rise of mHealth apps

The Rise of mHealth Apps: What are mHealth apps and what is causing their market growth?
Mobile Health apps better known as mHealth apps are in a rapidly growing market and is covered by three main app types.
- Disease and treatment management
- Wellness Management
- Others
Disease and Treatment Management apps
Disease and treatment management apps provide support, information and tools relating directly to healthcare, managing treatment and supporting patient conditions.
Some of these may include apps produced by healthcare providers or apps created to promote and maintain Women’s health.
Wellness Management apps
Wellness management apps are designed to aid users in achieving their objectives and making lifestyle adjustments, such as managing their diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing or reducing stress.
Typically, these applications are offered or created by organisations focused on fitness, nutrition, and mental well-being. While they are not directly connected to primary healthcare, they can serve as valuable tools to enhance user awareness and motivation regarding how these aspects influence their overall health conditions, whether positively or negatively.
Other mHealth apps
Others relates to mobile apps that fall outside of these main categories but that help users to manage or understand further factors interconnected to maintaining their health.
How has the market for mHealth apps grown?
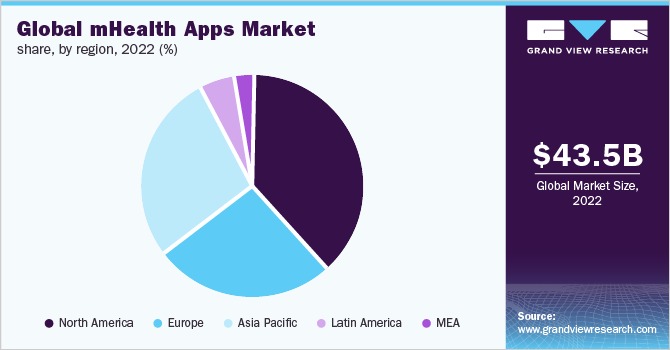
The global market for mHealth apps in 2022 was $49.2 billion and this is expected to reach $105.9 billion by 2030.
The breakdown by app types in 2022 looked like this.
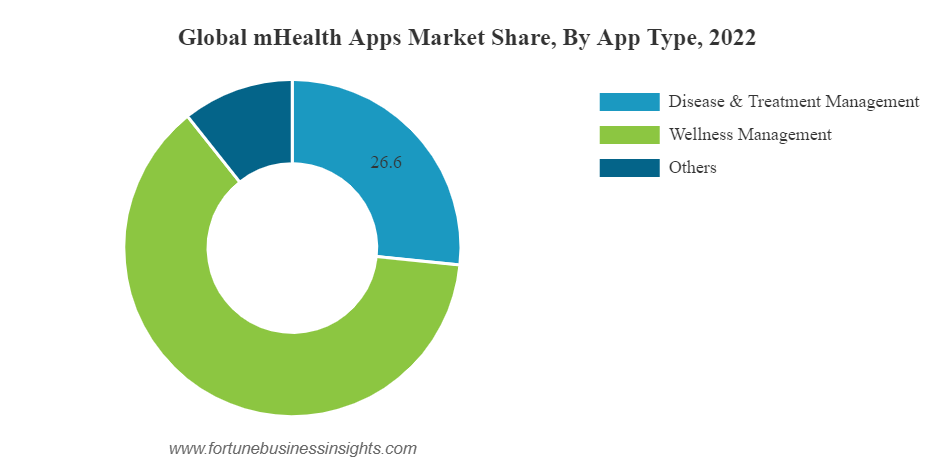
The regional market share in 2022 looked like this.
What is contributing to the mHealth market growth?
A number of varying factors have had a significant impact on the growth in popularity and usage of mHealth apps including the COVID-19 pandemic, increasingly sedentary lifestyles and obesity, and a drive to control or lower costs by primary healthcare providers through tools like appointment scheduling and associated reminders.
In addition to seeking solutions to manage the impact of the rise in chronic diseases through ongoing monitoring and more regular checkin activities, there have also been technological factors at play including the desire and willingness for patients and the general population to adopt and invest in emerging technologies such as wearables, some of which have been linked to early detection of disease developments. They have also been used in predictive studies such as the *Datenspende study where the regional probability of COVID–19 outbreaks was successfully predicted by incorporating wearable acquired data on pulse, physical activity (PA), and sleep, as well as weather data across a sample size of over 0.5million participants.
Other contributing factors in the successful implementation and access to such technologically advanced and connected apps is the widening availability of wireless internet carrier services, able to support an always connected ecosystem, such as 4G LTE and 5G. Such seamless uninterrupted and friction-free service will augment the experience for all mHealth app and wearable users which will in turn drive demand further, contributing to the expected global rise over the next 7 years.
Points of note and key takeaways:
A medical landscape of worsening and degrading health creates enormous cost implications to manage and treat affected patients. As such healthcare providers and advisors should be exploring the many potential cost saving benefits brought about through connected health and ongoing monitoring through data acquisition and even through simple to use patient specific recording of localised symptoms or patient medical journal entries.

Versus Arthritis app symptom journalling feature
Access to inexpensive and easily accessed monitoring technologies and tools creates desire and some level of personal goal-driven accountability to maintain and improve personal body metrics like heart rate, sleep patterns and energy consumption. When the path to adopt and use these tools is not cost prohibitive or requires significant user training or support material, the general population is likely to embrace apps that leverage the capabilities within mobile devices and wearables to deliver and support healthcare benefits.
As the understanding of the advantages offered by mHealth apps continues to grow, and their capabilities evolve to efficiently deliver healthcare data, information, treatment recommendations, directly to users via smartphones, this trend becomes increasingly significant for governments, especially in fields like disease control and health promotion. This was notably demonstrated by a substantial 46% surge in mHealth app adoption in Europe during 2020. This surge was primarily driven by the widespread adoption of government-supported COVID-19 tracing and warning apps.
As data acquisition technologies advance, alongside improved internet connectivity and growing awareness of the health benefits for various chronic diseases, primary healthcare providers and complementary wellness and fitness businesses are poised to leverage these advancements. They will harness these opportunities to generate cost savings and explore new avenues for revenue growth through innovation and enhanced user experiences with reduced friction.
Sugar Rush have a pedigree of developing mobile apps across a wide variety of industries including disease and condition management and are well versed in leveraging the embedded technologies within smartphones and wearables to support a range of commercial applications and needs.
For more information contact us and see how we can help with your mHealth project.
*Robert Koch Institute Corona-Datenspende | Robert Koch-Institut. Corona Data Donation. 2020.